AtOsteochondrosis of symptoms and treatment of cervical spine and treatmentThey will be different depending on the type of deformity in the cervical vertebrae obtained in connection with a long physical, inflammatory or mental effect on them.

The disease is often chronic, manifested by many clinical symptoms caused by the drainage of nerve roots and blood vessels that exit the vertebrae. Their compression is due to wear or deformation of the intervertebral discs (reducing their height, loss of elasticity, deformation of the fibrous ring or destruction). Cervical osteochondrosis is a common disease that occurs at any age after 20 years.
The cause of the pathology is the destructive changes in the spine. First, changes occur in the intervertebral discs: their elasticity, strength and reduction of height, their fibrous ring is deformed, convexities (the initial stage of the intervertebral hernia) and hernias appear. All these changes cause the growth of the bones of the vertebrae (osteophytes), leading to displacement, and later - to the loss of mobility of the cervical vertebrae. Because the spine is a flexible protective "case" for the spinal cord, the destructive changes in the intervertebral discs, and the loss of flexibility of the vertebrae are detrimental to the nerve and vascular structures of the spinal cord. They are the subject of drainage, a displacement that disrupts the cerebral circulation and the innervation of not only the cervical and shoulder areas, but also the internal organs, the lower limbs.
The more adherent the patient is, the more intervertebral discs are changed under the influence of muscle weight loss associated with age, long loads of the spine, injuries, slowing down physical activity, incorrect posture, stressful situations and increased tension in the neck, shoulders, inflammatory diseases.
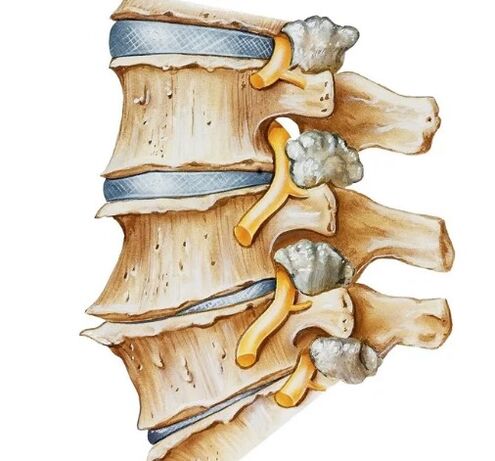
Due to its anatomical structure, the cervical spine is more proposed to pathology, since its vertebrae are the most movable and very tightly arranged with each other. In addition, cervical vertebrae have low muscle protection. Most often, degenerative changes develop in the intervertebral discs of the most movable 5. 6, 7 cervical vertebrae.
What are the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Variety and discrepancy of symptoms
Osteochondrosis of symptoms and treatment of cervical spine and treatmentIt must be considered in comprehensive and jointly with the type and severity of the degeneration of the intervertebral discs. The signs of cervical osteochondrosis are diverse and contradictory, as they depend on the location and power of manifestation of the process of deformation of the intervertebral discs, the peculiarities of compression or the pressure of the nerve roots and blood vessels, as well as the location of the muscles and organs, with them with their blood.
Therefore, often patients' complaints are not directed to a neurologist, but to other specialists: cardiologist, therapist, otolaryngologist, optometrist, rheumatologist and more. For example, complaints of dizziness, pain in the shoulder joint or noise in his ears, darkening in the eyes, patients do not associate pathology in the neck of the neck. At the same time, the neuropathologist may diagnose cervical osteochondrosis based on the results of brain and spine NMR, ultrasound of the brain of the brain, ECG and others.
Three sets of signs of impaired nervous system function
Experienced specialists know about thirty different options a combination of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis. It will not be possible to describe all signs of manifestations of this general disease so let's focus onthree complexesThe main symptoms characterizing certain impaired function of the central nervous system.
The first complex of major symptoms is used for impaired function of the peripheral section of the nervous system. This department is represented by nerves and other elements that leave the brain and spinal cord and are divided into somatic and autonomous systems.
In short, the first complex of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis is represented in the form of different localization of pain. This does not mean that the signs are only painful, often the pain is combined with other impaired body functions. But mainly - these are constant or periodically onset of neck pain, the appearance of which the patient is associated with hypothermia, prolonged stress or in uncomfortable posture, lifting of weights, a sharp turn of the head.
Pain is pain, shooting or shock -like. Their location depends on the tension of certain muscles associated with specific nerve roots that are squeezed by the vertebrae. Therefore, the pain can spread in the neck, nape, shoulder, one or two hands, radiates to the chest - in the heart, liver. In addition, in the vertebrae of the cervix of the cervix of the cervix there are complaints of crunching when the head moves, as well as the stiffness of the rotating movements of the head.
In the acute onset of the disease, the pain and spasm of the neck muscles force the patient to be in the posture with a tilted head and turned aside. Burning pain can occur between the shoulder blades if the cervical vegetative formations are compressed and their blood supply is impaired. Such pains usually increase with physical and emotional stress.
Often there is swelling, paleness and cooling of the hands, their tingling, rapid heart heart rate, heart pain, narrowing or expansion of the pupils, etc. Due to impaired innervation of the shoulder and spatular region, symptoms of a dystrophic change in the shoulder joint may occur. Patients complain of pain, the inability to lift and take the arm from the side, the stiffness of the shoulder joint.
The second complex of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis occurs due to impaired spinal cord function and is manifested by motor disorders.
Disorders of the spinal cord function occur due to its compression as a result of the loss of pulpulated nucleus from the disc or injury with hard disks and outgrowths (osteophytes). Depending on the mechanism of exposure to the spinal cord, the following complex of motor disorders is noted: the firmness of the occipital and cervical muscles, the weakness of the arms and legs, with an increased tone of the muscles of the legs and reduced tone and weight loss; loss of fever and sensitivity to pain; Severe leg fatigue, impaired coordination.
The third set of symptoms characterize the disorders of blood supply to the vessels of the brain and pathology of the cranial nerves that occur due to deformities in the cervical vertebrae. Symptoms of vascular pathology are manifested.
Characteristic symptoms of vascular disorders:
- neurotic conditions (irritability, longing, anxiety, fatigue, sleep disorders);
- seizures; headache and dizziness; nausea and vomiting;
- noise and ringing in the ears, hearing loss;
- visual disorders (darkening in the eyes, fog, flickering points, visual impairment);
- Slavic yield syndrome (sore throat, feeling of foreign object, dryness, difficulty swallowing).
The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are not unambiguous and should be considered in the complex and depending on the pathological processes in the spine.
Only a qualified specialist can cope with the clinical manifestations of this disease, make the right diagnosis and prescribe the proper treatment of the causes of discovered disorders.
How to treat this disease
Osteochondrosis of the symptoms and treatment of the cervical spine depends on the condition of the patient, the severity of the disease, the nature of the damage to the cervical vertebrae.
In the acute period, hospitalization and medication treatment may be required. Usually use analgesics, muscle blockade of novocaine, muscle relaxants that relieve muscle spasm; Chondroproprotectors for feeding cartilage tissue; Sedative drugs that soothe the nervous system, B vitamins, increase the muscular conductivity. The treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is always long and should be complicated.
During periods of remission, when acute symptoms are absent, physiotherapy methods (electrophoresis, ultrasound, etc. ), therapeutic physical education, massage, and non -traditional procedures, for example, acupuncture are widely used.
Many conservative methods for the treatment of osteochondrosis are known that can stop the progression of the disease. However, each patient needs an individual course of treatment, taking into account the stage of the disease, body characteristics, gender and age. The purpose of treating cervical osteochondrosis is:
- Elimination of pain and edema at the site of inflammation.
- Relaxation of the tense neck muscles.
- The release of secured nerve roots.
- Increased blood circulation.
- Activation of metabolism.
- Improve the power of intervertebral discs.
Target complex treatment can prevent the onset of convexity and intervertebral hernias.
In order not to start symptoms and treatment osteochondrosis and treatment and severe complications of the disease should begin to start timely treatment.

























